Join our next live session with Nacha on modern, programmable ACH on February 12th.Register here →
ISO 20022 files are a collection of XML-based schemas which standardize any type of financial message.
From payment clearing and settlement to account management, ISO 20022 files cover a diverse range of communications. Through consistent names and placements for each message’s attributes, all parties can rely on the same language.
How do ISO 20022 files work?
Every day, financial institutions, businesses, and banks exchange innumerable messages with private information regarding initiating payments, managing ATM transactions, or reporting fraud. ISO 20022 files facilitate this transfer, offering a universal format for domestic and global financial communication.
Every ISO 20022 file has a specific four-part identity, signifying its category, type within that category, variant, and version. These categories are four-character identifiers indicating the message’s broad classification, such as cash management, camt; securities clearing, secl; and ATM card transactions, catp.
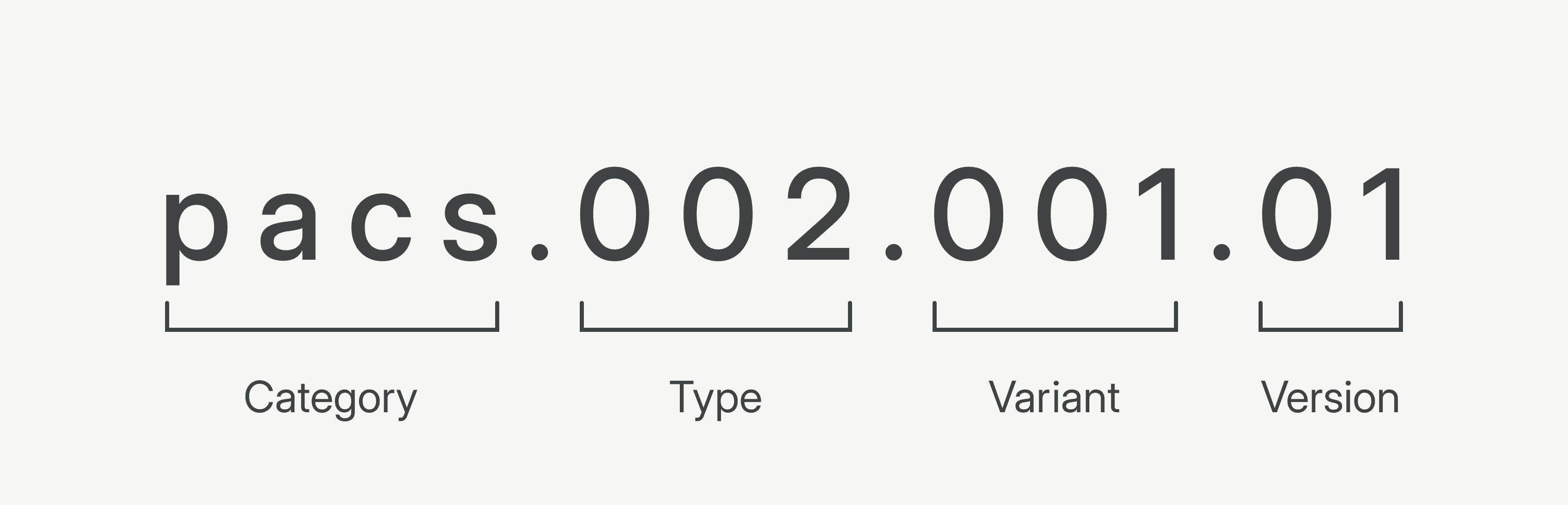
Per the image above, if a bank wants to send an update about the clearing or settlement status of a payment, they can create an ISO 20022 file within the payment clearing and settlement category with the identity, pacs.002.001.01.
What are the origins of ISO 20022 files?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO), created the ISO 20022 file format, a standardized communication framework for a global financial system. Before developing ISO 20022 files, payment systems around the world used their own proprietary file formats to communicate. Even the European ACH system and US ACH system used different file types.
For multinational transactions, financial organizations had to translate each region’s domestic format for payment rails like wire transfers, RTP, and ACH to be mutually understood. The only exception was SWIFT, which standardized international financial messaging using MT files that summarize transactions in a daily statement. In today’s globalized economy, ISO 20022 files incentivize domestic payment systems to evolve with the interconnected movement of funds.
Who uses ISO 20022 files?
The majority of real-time gross settlement networks and high-value payment systems have adopted or plan to adopt ISO 20022 files, including Europe’s EURO1, UK’s CHAPS, Fedwire, CHIPS, and SWIFT. Even real-time systems and low-value payment systems are either migrating to ISO 20022 or translating their files into the new format.
Most domestic payment systems across the globe will embrace ISO 20022 files within the next one to three years, and it’s expected that it will become the worldwide standard by 2025. This change has important implications for the future of money movement. The use of ISO 20022 files moves the world one step closer to a fully globalized financial system, prompting businesses, financial institutions, and banks to adapt to stay competitive.
Today, banks mainly use ISO 20022 files to communicate with each other. As these files become financial mainstays, companies can expect to interact with them more often. Banks may even ask businesses to prove their ability to communicate in this format and draw up ISO 20022 files. This shift to ISO 20022 reduces the inefficiency of translating one file type to another and facilitates more robust financial messaging.
What are the benefits of ISO 20022 files?
The creation and widespread adoption of ISO 20022 files marks a historic development in the evolution of money movement. By standardizing the representation of data, names, and addresses, ISO 20022 files increase message precision and prevent information loss between parties. They also have distinct implications for financial institutions and businesses.
Standardized financial messaging allows financial institutions to conduct complex multinational transactions across the global financial network. For these institutions, ISO 20022 files improve interoperability between payment systems and offer new functionalities. These files provide information about the ultimate originator and recipient of a payment involving up to four parties. Compared to more limiting file formats, ISO 20022 files can provide more context about payments like unit prices, quantities, and invoice descriptions.
Learn
Explore the fundamentals behind back office finance processes and the accounting principles underlying them.
Gross merchandise volume (GMV), also known as gross merchandise value, is the total value of the goods or services retailers sell over a set period.
ISO 20022 files are a collection of XML-based schemas which standardize any type of financial message.
Month-end close is a critical process where the accounting team reviews and records financial transactions to close out the month.
While both are essential for managing online transactions, there are several differences between payment processors vs. payments gateways.
Revenue recognition is a key accounting principle in which a company records its revenue as it earns it, not necessarily when paid for.
Treasury Management Systems (TMS) are software applications that serve to help businesses simplify their payment operations by automatically tracking things like cash flow, assets, investments, and more.
BAI2 files are a cash management reporting standard. They are widely accepted by banks across the United States for exchanging data regarding balances and transactions.
Incoming payment details are notifications that a company is going to receive a payment it didn’t originate—meaning the receiving funds were not initially requested.
Nacha files are the standardized file format that banks use to initiate and manage batches of ACH payments. These files help banks execute large volumes of ACH payments through The Clearing House (TCH) and Federal Reserve.
Payment controls help accounts payable (AP) departments avoid losing money due to fraud, late payment fees, and other errors. They are a necessary part of a company’s overall payment operations to keep payments secure, accurate, and authorized.
Account-to-Account (A2A) banking, sometimes also called Me-to-Me banking, is the transfer of funds from one account to another account.
Asset risk management is essentially a fusion of asset management and risk management.
Bank reconciliation is the process of verifying the completeness of a transaction through matching a company’s balance sheet to their bank statement.
Batch processing is a method of processing various types of transactions. As the name suggests, transactions are processed in a group or “batch.”
In business terms, float refers to the time delay between the movement of funds from one account to another.
Cash forecasting is a way for companies to look at “cash in” vs. “cash out” for a business over a window of time.
Cash management is the monitoring and maintaining of cash flow to ensure that a business has enough funds to function.
Cash pooling is a centralized cash management tool that companies with multiple subsidiaries sometimes use to optimize the cash balances of all legal entities.
The term "cash position" pertains to the quantity of cash or assets that can be readily converted to cash, held by an individual, company, or financial institution at any given moment.
Continuous accounting is the ongoing process of updating a business’s general ledger with reconciled bank statement transactions as soon as they become available.
Electronic check presentment (ECP) is the process of electronically submitting a check to a bank for payment.
IBAN, or an International Bank Account Number, makes it easier and faster for banks to process cross-border financial transactions.
Liquidity management provides visibility into cash positions over past, present, and future dates and provides an overview of the financial health of a business.
Payment operations is an umbrella term that refers to the entire lifecycle of money movement for a company.
Recoupment refers to the recovery of spent or lost funds, especially in business operations.
Two options for financial transaction settlement—differing in both speed and style—here, we’ll look at how both Net Settlement and Gross Settlement work in action.
Treasury management is the act of managing a company’s daily cash flows and larger-scale decisions when it comes to finances.
A banking API is software that facilitates a digital connection between a company and a bank.
Popular in the banking and finance world, penny tests are a simple way to verify the validity of a bank account or bank integration, prior to a large finance transaction taking place.
Sweep accounts are a particular type of bank account where funds are automatically transferred between different accounts to optimize the use of available cash and maximize returns
Identity Verification APIs allow businesses to streamline the process of checking the identities of new users by automatically, and in some cases instantly, verifying their provided identifying information.
An invoicing API allows companies to create, send, manage, and reconcile invoices, as well as track related payments end to end.
The issuer identification number (IIN) is the first eight or nine digits on a payment card tied to the financial institution that issued the card.
An MT940 (Message Type 940) file is a detailed SWIFT statement that provides information about account transactions.
An OFAC check is a screening process used by financial institutions, businesses, and government agencies to ensure that individuals or entities involved in a transaction are not listed on sanctions lists maintained by the U.S. Department of the Treasury's Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC).
The Flow of Funds is the movement of money in and out of bank accounts.