Join our next live session with Nacha on modern, programmable ACH on February 12th.Register here →
Behind The Scenes: How Modern Treasury Ensures Payment Security
Security is the foundation for Modern Treasury operations and software. This article explores what we’ve implemented over the years to help enterprises move, track, and reconcile money securely.

Securing Communication with Our Bank Partners
As an independent software layer on top of client bank partners, safeguarding communication between Modern Treasury and banks is imperative. This demands a robust framework for auditing and hardening the network connections between banks and our customers. While the exact configuration of defenses may differ slightly from bank to bank, Modern Treasury ensures the most secure setup available for every bank integration.
Cryptographic Protection with TLS v1.2
A key element to secure communication is a cryptographic protocol. Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts data exchanged between our systems and banks—it also authenticates identities, ensuring that information remains confidential during transit.
TLS has evolved substantially since its inception. In today's cybersecurity landscape, TLS v1.2 is a non-negotiable requirement. At Modern Treasury, TLS v1.2 is deployed and mandated across all connections.
The prevalence of legacy systems throughout the industries we serve made enforcing a minimum of TLS v1.2 (and dropping support for older versions) challenging. We spent much of 2023 working closely with banks to transition safely, and Modern Treasury applications have been updated to enforce this requirement in code.
Close relationships with banks allow our team to advocate for security improvements and collaborate with bank partners to implement changes.
Securing Inbound Connections
Modern Treasury uses several layers of defense in addition to TLS.
IP allowlist
With a list of recognized IP addresses, our team ensures that all incoming communication from banks originates from expected sources. Because our systems only recognize and accept connections from trusted IP addresses associated with our bank partners, Modern Treasury has established highly targeted access control. This not only mitigates the risk of unauthorized access but also supports observability for network traffic management.
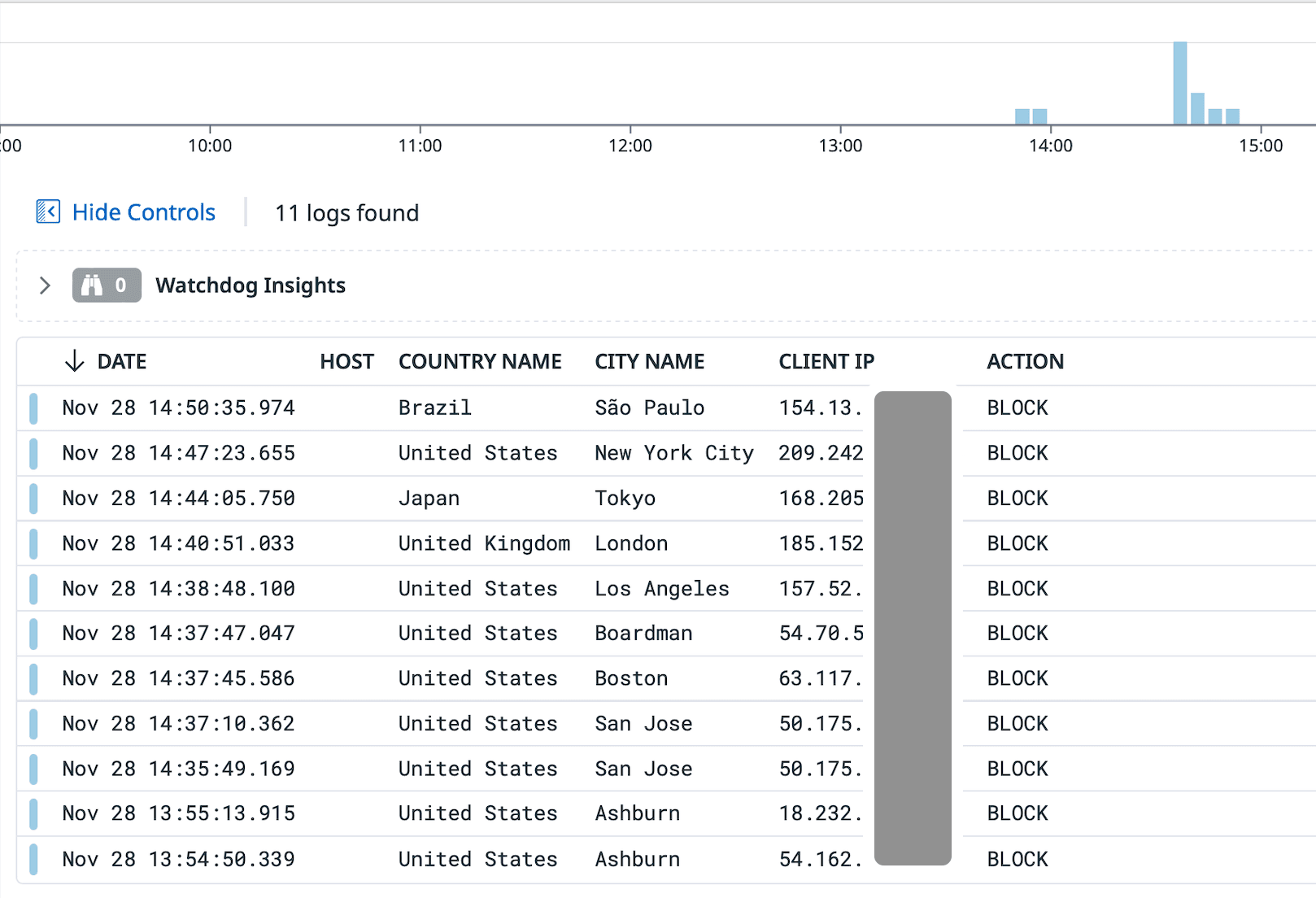
Requests from unknown sources blocked by IP allowlist
Leveraging relationships with our bank partners allows Modern Treasury to obtain and maintain a comprehensive and static allowlist of IP addresses, ensuring comprehensive coverage across inbound connections.
Message Signature Verification
When a bank sends a message to Modern Treasury, it uses a shared secret to cryptographically sign the message. Modern Treasury then employs the same secret to verify the authenticity of the signature and integrity of the message body. This is done on top of cryptographic signatures within TLS.
Message Signature Verification not only ensures the authenticity of every message but also establishes non-repudiation, a concept that enhances accountability and trust. With non-repudiation, a sender is prevented from denying their involvement in a communication, thereby adding an extra layer of assurance.
Some bank partners use an asymmetric key instead of a shared secret, which Modern Treasury also supports.
Securing Outbound Connections
Similar to our approach for inbound connections, Modern Treasury works with bank partners to implement IP allowlisting and signature verification strategies for outbound communication.
IP allowlisting
We adopt a proactive stance by providing banks with a list of IP addresses that are owned by Modern Treasury and registered with the American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN). Owning registered IPs affords us additional control and stability, a significant advantage over IPs associated with cloud providers. IP addresses registered to cloud providers risk being accidentally released or maliciously taken over.
Bank Server Fingerprinting
Internet-based network communications are always at risk for a DNS takeover.
A DNS takeover is a security vulnerability in which an attacker gains control of a domain's DNS settings, redirecting the traffic intended for that domain to a malicious server under the attacker’s control. In our context, if an attacker successfully executes a DNS takeover on the bank's domain, they could reroute Modern Treasury to a fraudulent endpoint of their choosing. This would be a serious data breach.
To mitigate this and other associated risks, our team employs preventative measures that we refer to collectively as “Bank Server Fingerprinting.” These techniques involve recording metadata from bank servers, including their TLS certificates, SFTP and SSH host keys, and IP addresses. Modern Treasury logs all of this for every connection with bank partners.
We have also set up automated detection to track changes to this identifying metadata for each bank’s endpoint. If any anomalies are detected (e.g. a change in the bank’s TLS certificate authority or SSH fingerprint), a comprehensive investigation is triggered.
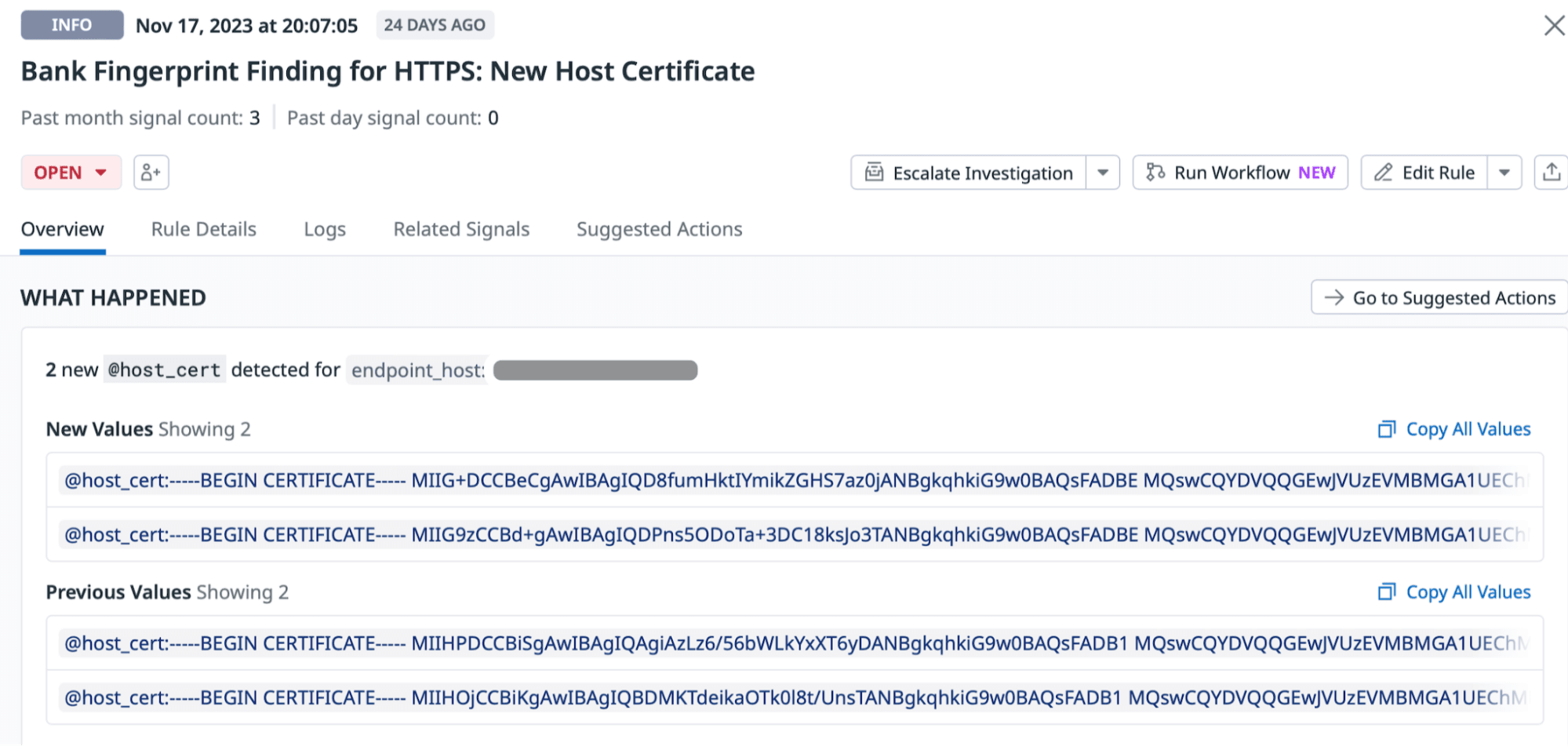
Alert of bank servers’ metadata change. In this case, the bank had rotated their server certificates.
This acts as an early warning system. It allows our team to swiftly investigate and address potential compromises, mitigating the impact of security threats before they escalate.
We have dedicated security on-call personnel who triage and respond promptly to any identified anomalies. This response capability ensures that potential security incidents are addressed in real-time, minimizing the window of exposure. In these moments, our relationships with bank partners also help us address potential security threats collaboratively.
A Strong Compliance Posture
Several industry-leading certifications validate Modern Treasury’s commitment to rigorous security controls across the product.
PCI DSS 4.0: Upholding Payment Security Standards for Card Transactions
Our compliance with PCI DSS 4.0, explored in detail here, confirms our commitment to safeguarding payment card information.
SOC 2 Type II: Trust and Transparency in Security Processes
In order to achieve SOC 2 Type II compliance, Modern Treasury’s information security controls and processes underwent thorough assessment. This certification, granted by an independent auditing firm, confirms that our solution’s security measures align with industry best practices.
SOC 1 Type II: Financial Controls and Operational Transparency
SOC 1 Type II certification emphasizes our dedication to financial data integrity and operational controls. Independent auditors assessed the effectiveness of Modern Treasury’s financial reporting processes, providing assurance to clients and partners that our operations meet or exceed industry standards for financial controls.
Payments Security at Modern Treasury
Modern Treasury’s commitment to partnering with banks and attaining vital certifications are just a few facets of our overarching dedication to holistically protecting customer data, our cloud infrastructure, and our business operations. For more information, visit our security page which includes detailed security protocols, from data encryption to access controls and beyond.
To explore how enterprises use Modern Treasury to move, track and reconcile money safely at scale, reach out to us here.