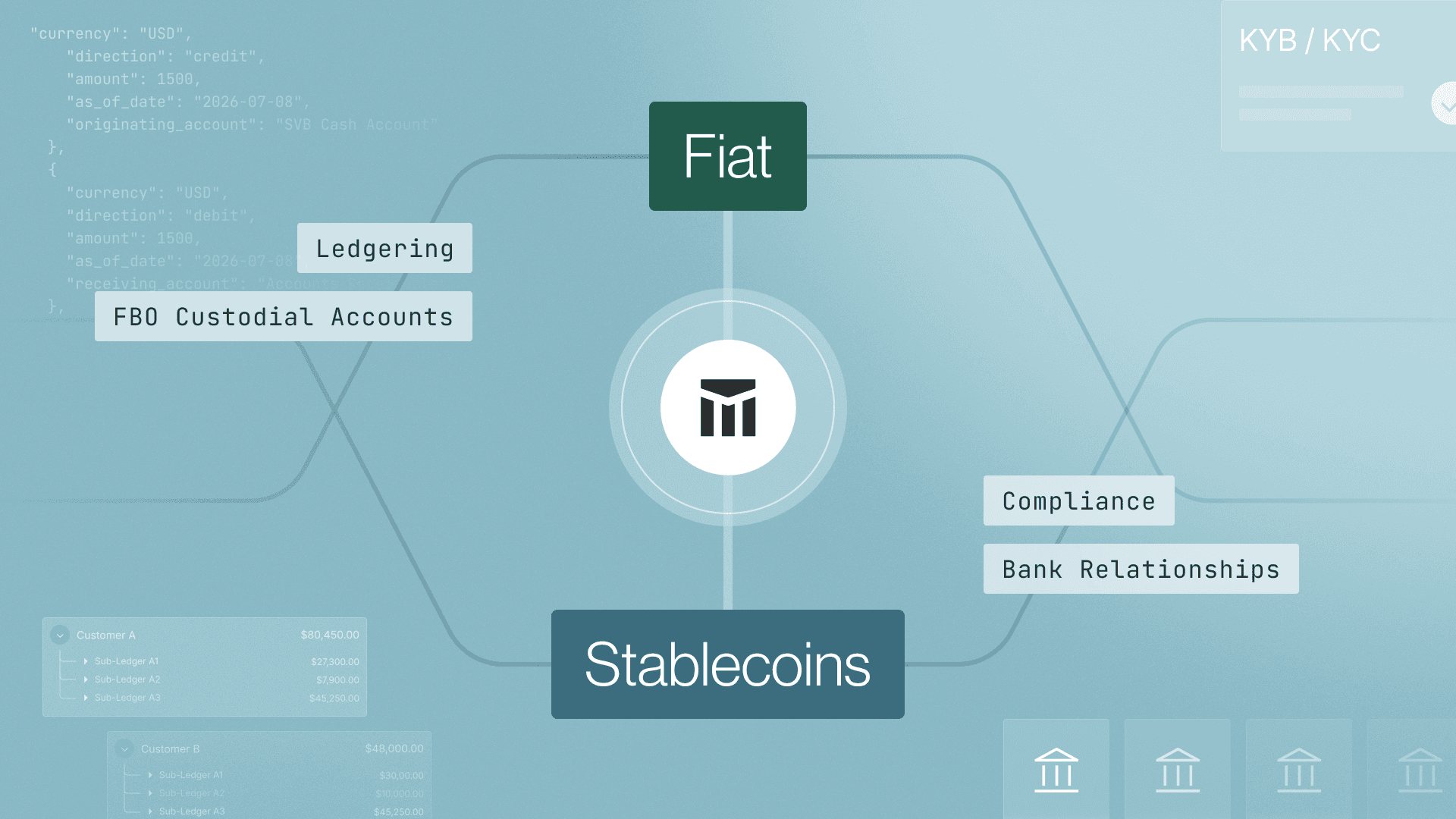
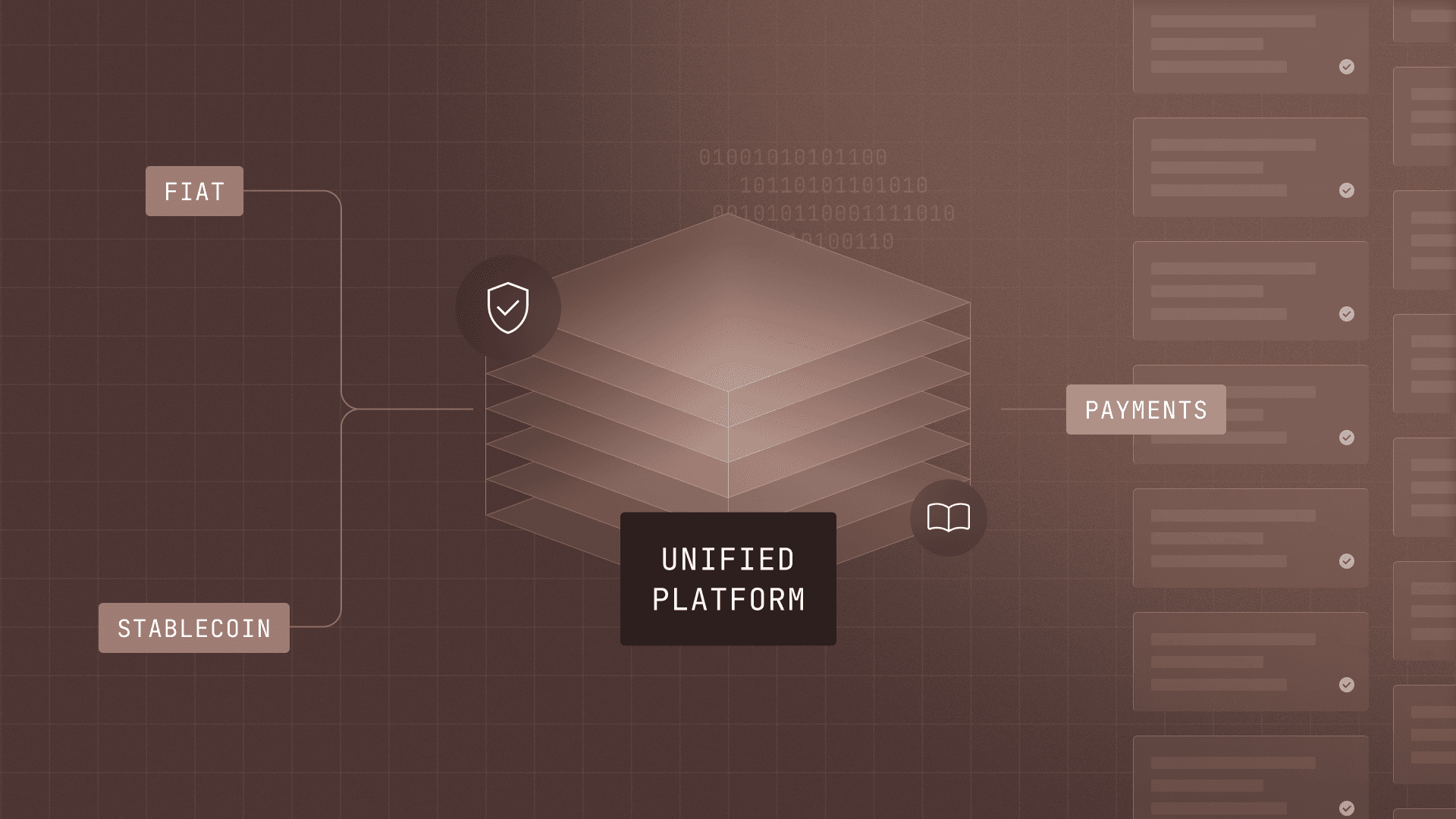
Introducing Modern Treasury Payments. Built to move money across fiat and stablecoins. Learn more →
How Do Banks Report Balances and Transactions?
If you need to track the complete lifecycle of a payment from the time it is approved and sent to the bank, through completion, you need to reconcile it to a cash transaction. A bank statement is precisely what’s needed: a chronological list of credit and debit transactions with corresponding bank balances at any point in time.

The majority of money movement in the United States happens via ACH, wire, and paper check, and is transmitted through corporate bank accounts. To track those payments, a company will follow it through the complete lifecycle: from the time it is approved and sent to the bank, through to completion. Ultimately it will be reconciled to a cash transaction.
Background
A bank statement is precisely what’s needed: a chronological list of credit and debit transactions with corresponding bank balances at any point in time.
For automatic reconciliation, and to allow our customers to view their balances as they update throughout the day, we receive and process bank statements, or “balance and transaction reports.” These reports are sometimes also called “bank feed,” “bank connectivity,” or “direct transmission reporting.”
Modern Treasury uses industry-standard file formats to access this type of information from a bank. This article will provide a look under the hood of three of the most popular types of files, transmitted between banks, corporates, and technology partners to enable the tracking of billions of dollars.
BAI2
BAI2 is one specification for .txt files that banks offer to clients for balance and transaction reporting. Created by the Bank Administration Institute to standardize balance reporting in 1986, BAI2 is the successor to BAI1 (released in 1980) and Lockbox Communication Standards for Banks (released in 1971). Among other things, it records individual transactions using hundreds of codes to describe balances and deposits, as well as inbound and outbound payments.
In 2008, the copyright to BAI was transferred to Accredited Standards Committee X9, which enhanced BAI2 in 2016 and renamed it to Balance and Transaction Reporting Standard (BTRS). BTRS is compatible with BAI2 and nearly architecturally identical, with the distinction being the removal of a number of BAI codes from the BTRS specification. Many banks in the United States still transmit BAI2 files, and the specification is near universal in the United States for banks that provide corporate treasury services.
MT940
MT940 is a specification developed by the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT), which is the registration authority for many ISO standards for banking messaging. MT940 shares similarities to BAI2/BTRS file specifications, but is standard outside of the United States, especially in Canada and Europe. It only supports prior day, rather than intraday reporting. Another SWIFT format, MT942, reports bank balances, but acceptance of either of these standards is dependent on the bank.
Options Vary By Bank
It’s worth noting that how frequently you can receive these files is at the discretion of the bank that creates them. Many of our supported banks have the ability to transmit BAI2 or MT942 files multiple times a day, and frequencies vary too. File format support is also determined by your bank, so you should consider your necessary capabilities as you choose a financial institution: if you need reporting on balances and transactions throughout the day, it may be helpful to bank with a provider that offers BAI2 or MT942 support for their Direct Transmission services.
Conclusion
Standardized bank reporting files enable companies to receive balance and transaction data systematically. If you initiate payments at scale and need to track those transactions, consider getting bank data through BAI2 or MT940.
As a software layer between companies and their bank, Modern Treasury enables businesses to manage the movement of money at scale, including reconciling payments to cash transactions across one or multiple banks. If you’re interested in programmatic payments and taking the guesswork out of bank-specific file formats, send us a note.